What is Infrared (Thermal) Emittance?
Passive design strategies directly impacts heat gain or heat loss without relying on mechanical systems or active systems. Selecting materials wisely is one of the methods to apply passive design strategies.
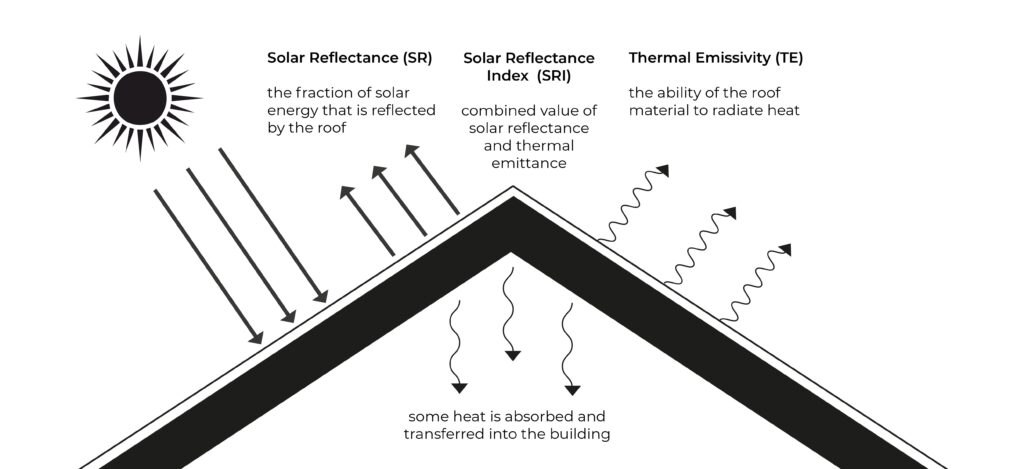
Infrared Emittance is a material’s ability to emit absorbed heat as infrared radiation. Especially in passive design strategies, it is an important feature, affecting the thermal performance of buildings.
Emittance, or emissivity, is a measure ranging from 0 to 1 that describes how effectively a material can release heat in the form of infrared radiation. It is defined as the fraction of energy a material emits compared to that emitted by an ideal black body, a perfect emitter of heat with an emissivity value of 1. In contrast, a material with an emissivity of 0 behaves as a perfect thermal / infrared mirror, reflecting all thermal radiation without emitting any.
- High-emittance materials release heat, useful in hot climate to prevent overheating.
- Low-emittance materials retain heat, useful in cold climate to provide heat gain.
Why is Emittance Important for Buildings?
It plays a crucial role in cool roofs, facade, thermal mass performance, and envelope strategies.
Roofs get hot under the sun, and thus it is important to select materials that can release that heat effectively to keep the buildings cooler and reduces the need for air conditioning systems. Cool roofs, therefore, should have high thermal emittance to radiate the heat away.
Most building materials have high emittance value about 0.9 or 90%, and so they are very good at releasing heat. However, clean, shiny materials such as untarnished galvanized steel or aluminum foil are bad at emitting heat, but they reflect heat instead. On the other hand, aluminum coatings are not as bad as clean metals, they fall between in terms of emittance value.
Wavelength Range
The thermal radiation emitted by roofs and walls typically falls within the 5 to 40 micrometer wavelength range. Most common building materials, such as concrete, brick, and glass, are opaque in this spectrum, meaning they do not transmit infrared radiation but instead absorb and emit it.
Emittance Values
| Materials | TE – Emittance Value | Ability to Radiate Heat |
| Concrete | 0.92 | Very High |
| Clean Metals | 0.1 – 0.2 | Very Low |
| Aluminium: anodised | 0.77 | High |
| Aluminium: polished | 0.05 | Very Low |
| P.V.C. | 0.91 – 0.93 | Very High |
| Plaster | 0.86 – 0.90 | Very High |
| Plywood | 0.86 | Very High |
| Human Skin | 0.95 – 0.98 | Very High |